Cells are defined as the smallest functional unit of an organism. An organism is an individual life form, so cells are living.
Prokaryotes
- Simple cells
- No nucleus
- No membrane-bound organelles
- Bacteria

Eukaryotes
- Complex cells
- Have a nucleus
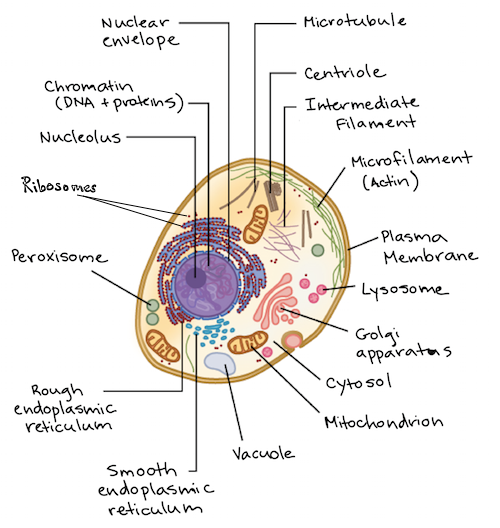
- Have membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), golgi apparatus, vacuole, and lysosome.
- Protists, fungi, plants, and animals
Both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have…
- Cell Membrane: Helps maintain homeostasis by controlling what goes in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: The jelly-like fluid in the cell that helps keep the organelles in place.
- Ribosomes: Create proteins for the cell.
- Cell Wall: Only found in plant cells. Gives them support and structure.
Endosymbiotic Theory
- A theory that states that long ago, free living bacteria were eaten by other eukaryotic cells and lived together. The engulfed bacteria later became parts of the cells we know today as the mitochondria and chloroplast.